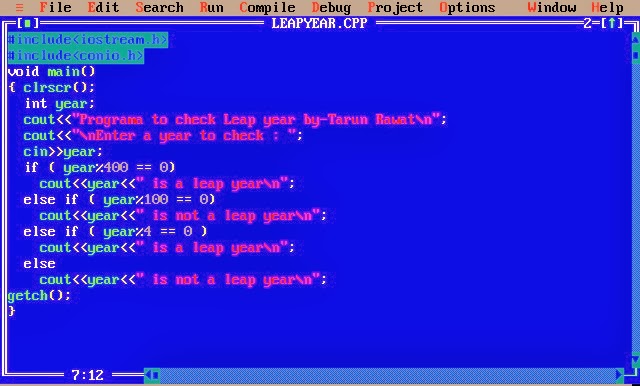
Leap Year Program In Dev C++
- C++ Basics
Easy Tutor author of Program to find whether a year is a leap year or not is from United States.Easy Tutor says. Hello Friends, I am Free Lance Tutor, who helped student in completing their homework. Waves l2 vst plugin download. I have 4 Years of hands on experience on helping student in completing their homework. I also guide them in doing their final year projects. Jun 08, 2015 How to check leap year using conditional operator in C programming. Write a C program to input year and check it is leap year or not using ternary operator. Learn C programming, Data Structures tutorials, exercises, examples, programs, hacks, tips and tricks online.
- C++ Object Oriented
Leap Year Program In Dev C Youtube
- C++ Advanced

- C++ Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
Leap Year Program In Dev C Pdf
The C++ standard library does not provide a proper date type. C++ inherits the structs and functions for date and time manipulation from C. To access date and time related functions and structures, you would need to include <ctime> header file in your C++ program.
There are four time-related types: clock_t, time_t, size_t, and tm. The types - clock_t, size_t and time_t are capable of representing the system time and date as some sort of integer.
The structure type tm holds the date and time in the form of a C structure having the following elements −
C Program For Leap Year
Following are the important functions, which we use while working with date and time in C or C++. All these functions are part of standard C and C++ library and you can check their detail using reference to C++ standard library given below.
| Sr.No | Function & Purpose |
|---|---|
| 1 | time_t time(time_t *time); This returns the current calendar time of the system in number of seconds elapsed since January 1, 1970. If the system has no time, .1 is returned. |
| 2 | char *ctime(const time_t *time); This returns a pointer to a string of the form day month year hours:minutes:seconds yearn0. |
| 3 | struct tm *localtime(const time_t *time); This returns a pointer to the tm structure representing local time. |
| 4 | clock_t clock(void); This returns a value that approximates the amount of time the calling program has been running. A value of .1 is returned if the time is not available. |
| 5 | char * asctime ( const struct tm * time ); This returns a pointer to a string that contains the information stored in the structure pointed to by time converted into the form: day month date hours:minutes:seconds yearn0 |
| 6 | struct tm *gmtime(const time_t *time); This returns a pointer to the time in the form of a tm structure. The time is represented in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which is essentially Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). |
| 7 | time_t mktime(struct tm *time); This returns the calendar-time equivalent of the time found in the structure pointed to by time. |
| 8 | double difftime ( time_t time2, time_t time1 ); This function calculates the difference in seconds between time1 and time2. |
| 9 | size_t strftime(); Dev c 4.9.9.2 free download. This function can be used to format date and time in a specific format. |
Current Date and Time
Suppose you want to retrieve the current system date and time, either as a local time or as a Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Following is the example to achieve the same −
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
Format Time using struct tm
The tm structure is very important while working with date and time in either C or C++. This structure holds the date and time in the form of a C structure as mentioned above. Most of the time related functions makes use of tm structure. Following is an example which makes use of various date and time related functions and tm structure −
While using structure in this chapter, I'm making an assumption that you have basic understanding on C structure and how to access structure members using arrow -> operator.
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −